Learning-Modern-HPC-Software
HPC Learning Roadmap
Haibin Lai
12211612@mail.sustech.edu.cn
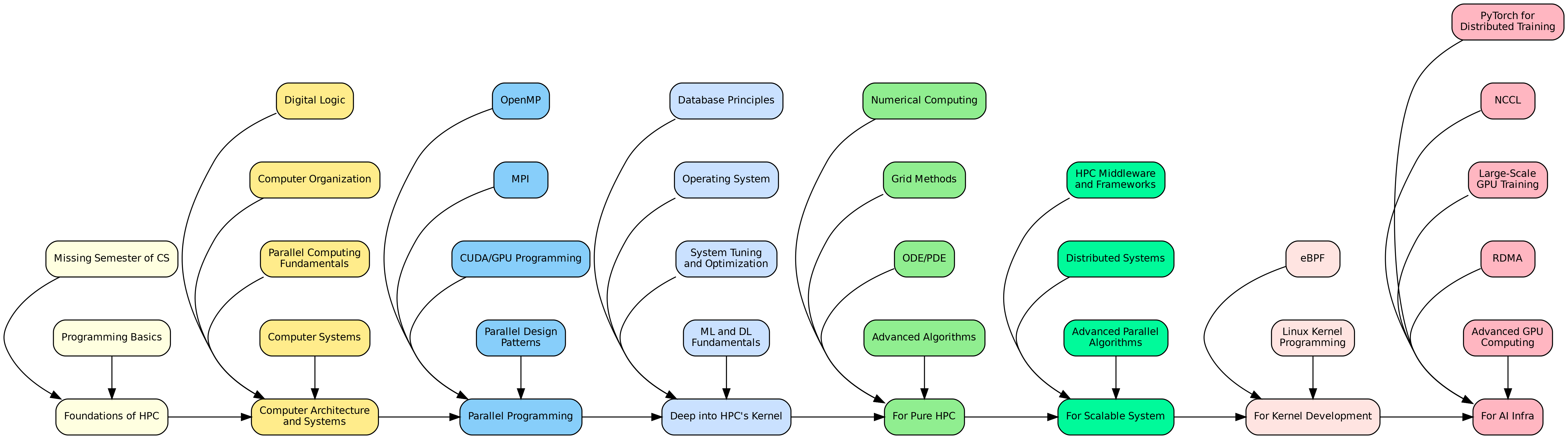
1. Foundations of HPC
After this step, you can connect to supercomputer and start your journey!
Missing Semester of CS Education:
-
Strongly recommend you to learn all the videos: 超算习堂
- The Missing Semester of Your CS Education
- Linux usage, IBM Spectrum LSF / Slurm usage
- git learn_git_branching
- shell, vim, gdb
Programming Basics:
- Learn Python, C, or C++ (common in HPC).
- Suggested: CS50’s Introduction to Computer Science (Harvard, edX) or Learn Python the Hard Way (online book).
2. Computer Architecture and Systems
After this step, you will know how programs run on our computer!
Digital logic:
Computer Organization:
- CPU, memory hierarchy, caches, pipelining.
- Computer Architecture: a quantitative approach
Suggested: Computer Organization and Design by Patterson & Hennessy (book or online lectures).
Parallel Computing Fundamentals:
- Concepts like Amdahl’s Law, parallelism types (task, data).
- 平行程式 周志远
Suggested: Introduction to Parallel Computing (online, University of Illinois via Coursera).
Computer Systems:
- How can C code runs on your machine?
- CSAPP link
3. Parallel Programming
- OpenMP:
- Shared-memory parallel programming in C/C++ or Fortran.
- Suggested: OpenMP Tutorials (Lawrence Livermore National Lab) or OpenMP official OpenMP
- MPI (Message Passing Interface):
- Distributed-memory programming for clusters.
- Suggested: MPI Tutorial by Wes Kendall MPI.
- CUDA/Parallel GPU Programming:
- GPU programming for NVIDIA hardware.
- Suggested: CUDA Programming (NVIDIA Developer Program, free).
- A must learn class if you want to do HPC research
- Parallel Design Patterns:
4. Deep into HPC’s kernel
-
Database Principles:
-
(CMU 15-445/645 & 15-721): CMU
-
Key topics: Relational models, storage architectures (heaps, log-structured), indexing (B+ trees, hash tables), transaction processing (ACID, concurrency control), recovery (logging, checkpoints), and parallel/distributed query processing.
-
- Operating System:
- Process management, memory management, scheduling.
- Suggested: Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces (free online book). OSTEP
- MIT 6.1810
- rCore
- System Tuning and Optimization:
- [2009.06489] The Hardware Lottery
- TMA top-down method
- Performance Analysis and Tuning on Modern CPU
- USB including CPU, memory, and I/O tuning.
- Profiling tools (e.g., perf, gprof, intel VTune), compiler optimizations (e.g., -O3, loop unrolling), and hardware-specific tuning (e.g., NUMA, cache-aware programming).
-
Machine Learning and Deep Learning Fundamentals:
-
Understand ML and DL basics, focusing on models and architectures relevant to HPC, where parallel computing (e.g., GPU clusters) accelerates training and inference.
-
Basic ML Models:
- Decision Trees, Support Vector Machines (SVM)
-
Key topics: Supervised learning (regression, classification), unsupervised learning (clustering), model evaluation (accuracy, precision, recall), and optimization (gradient descent).
- Suggested: CS229: Machine Learning (Stanford, lecture notes) or Machine Learning Crash Course (Google, free).
-
Deep Learning Papers:
-
AlexNet (2012): Introduces deep CNNs with ReLU, dropout, and GPU acceleration for image classification. Paper.
-
VGG (2014): Deepens CNNs with small (3x3) filters for improved performance. Paper.
-
ResNet (2015): Introduces residual connections to train very deep networks, reducing vanishing gradients. Paper.
-
Transformer (2017): Proposes attention-based architecture for NLP, scalable for HPC with parallel processing. Attention Is All You Need.
-
-
5. For pure HPC
-
Numerical Computing:
- Learn numerical methods for solving mathematical problems in HPC, focusing on accuracy, stability, and parallelization.
- Key topics: Floating-point arithmetic, numerical linear algebra (e.g., LU decomposition, iterative solvers), and optimization techniques (e.g., conjugate gradient).
- Suggested: Numerical Recipes (classic book, code in C/C++) or Introduction to Scientific Computing (UT Austin, free notes on numerical methods).
-
Grid Methods (Mesh-Based Techniques):
- Understand grid-based methods for discretizing computational domains in HPC simulations.
- Key topics: Finite difference methods (FDM), finite element methods (FEM), and finite volume methods (FVM) for solving PDEs.
- Suggested: Finite Element Methods for PDEs (SIAM book by Brenner and Scott) or Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations (Coursera, University of Michigan, covers FDM/FEM).
-
[Optional] Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations (ODE/PDE):
- Learn to solve ODEs and PDEs numerically, critical for HPC applications like fluid dynamics, climate modeling, and physics simulations.
- Key topics: Runge-Kutta methods for ODEs, explicit/implicit schemes for PDEs, and parallel solvers (e.g., domain decomposition).
- Suggested: Numerical Solution of Differential Equations (MIT 18.336, course materials) or DifferentialEquations.jl (Julia library with tutorials for ODE/PDE solvers).
- Note: Practice implementing solvers in parallel environments using MPI or OpenMP for scalability.
-
[Optional] Advanced Algorithms (MIT 18.337/18.338):
- Study advanced algorithms optimized for HPC, emphasizing parallel and distributed computing.
- Key topics: Parallel graph algorithms, sparse matrix computations, randomized algorithms, and high-performance data structures.
- Suggested: MIT 18.337J/6.338J: Parallel Computing and Scientific Machine Learning (course materials, lectures, and Julia-based projects) or MIT OpenCourseWare: Advanced Algorithms (focus on theoretical foundations).
- Note: MIT 18.337 uses Julia for numerical computing, which is highly relevant for HPC due to its performance and parallelization capabilities.
6. For scalable system
-
HPC Middleware and Frameworks:
- Explore middleware used in HPC clusters, such as job schedulers (Slurm, PBS Pro) and resource managers.
- Key topics: Workflow orchestration, containerization (e.g., Singularity, Docker for HPC), and cloud-HPC integration.
- Suggested: Slurm Workload Manager Documentation or SingularityCE User Guide.
-
Distributed Systems (MIT 6.824/6.5840):
-
big data idea: GFS ; big table ; map reduce
-
Key topics: MapReduce, Raft consensus algorithm, key-value stores, sharding, and distributed file systems (e.g., GFS, HDFS).
-
Suggested: MIT 6.824: Distributed Systems (course website, includes lectures, labs, and papers) or YouTube Lectures. Labs involve implementing MapReduce, Raft, and a fault-tolerant key-value store in Go.
-
-
[Optional] Advanced Parallel Algorithms:
- Study advanced algorithms for HPC, such as load balancing, fault tolerance, and scalable data structures.
- Suggested: Parallel and Distributed Computation: Numerical Methods (book by Bertsekas and Tsitsiklis) or Introduction to High-Performance Scientific Computing (free online book).
7. For kernel Development
- eBPF (Extended Berkeley Packet Filter):
- Learn eBPF for advanced performance monitoring, tracing, and system optimization in HPC environments.
- Key topics: Writing eBPF programs, using tools like
bpftraceandBCC, and monitoring system calls and network performance. - Suggested: eBPF.io (official eBPF resources) or Brendan Gregg’s eBPF Guide (tutorials and tools for performance analysis).
- Linux Kernel Programming:
- Key topics: Kernel modules, device drivers, memory management, and kernel-level debugging.
- Suggested: Linux Kernel Development (official Linux kernel documentation) or Linux Kernel Programming (book by Kaiwan N Billimoria).
8. For AI Infra
-
PyTorch for Distributed Training:
- Learn PyTorch to implement distributed training for AI models, enabling scalable deep learning on HPC clusters.
- Key topics: Data parallelism (using
torch.distributed), model parallelism, pipeline parallelism, and integration with HPC frameworks like MPI and NCCL. - Suggested: PyTorch Distributed Training (official PyTorch tutorials, covers
DistributedDataParallelandRPC) or Distributed Machine Learning with PyTorch (PyTorch Lightning tutorial on YouTube). Practice with Horovod for PyTorch-based distributed training on clusters.
Communication Part
-
NCCL (NVIDIA Collective Communications Library):
- Key topics: AllReduce, Broadcast, and AllGather operations, integration with PyTorch/TensorFlow, and RDMA support for low-latency communication.
- Suggested: NCCL Developer Guide (official NVIDIA documentation) or NCCL on GitHub (includes examples and setup for GPU clusters). Explore NCCL Tutorials for practical implementations.
-
Large-Scale GPU Training:
- GShard
- Key topics: CUDA programming for GPUs, multi-GPU training with frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow, and optimization techniques (e.g., mixed precision, gradient accumulation).
- Suggested: NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit Documentation (official CUDA resources) or CS231n: Deep Learning for Computer Vision (Stanford, includes GPU-based training labs). Practice with NVIDIA Deep Learning AI (free courses on GPU training).
-
RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access):
- Understand RDMA for high-performance networking in AI and HPC, enabling low-latency, high-throughput data transfers.
- Key topics: InfiniBand, RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet), GPUDirect RDMA, and their use in distributed AI training.
- Suggested: Introduction to RDMA Programming (Mellanox/NVIDIA guide) or High-Performance Computing with RDMA (HPCwire article). Explore NCCL’s RDMA support for GPU clusters.
Computing part
-
Advanced GPU Computing:
- PTX, SASS
-
bank conflict, warp divergence
-
Key topics:
-
Common Methods: Parallel thread execution, kernel launches, memory coalescing, and stream processing.
-
Optimization Tricks: Minimizing warp divergence (avoiding branch divergence within warps), resolving bank conflicts in shared memory, optimizing memory access patterns, and using asynchronous data transfers.
-
Principles: GPU architecture (SMs, warps, threads), memory hierarchy (global, shared, register), and latency hiding.
-
- Suggested: CUDA Programming Guide (official NVIDIA guide, covers warp divergence and bank conflicts) or Professional CUDA C Programming (book by John Cheng et al.). Explore CUDA Optimization Tips (NVIDIA blog on warp divergence and memory optimization). Some graph paper is also ok.